Why Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) are important
In modern software development, CI and CD play a pivotal role. To appreciate their significance, let’s first explore how the process traditionally functioned.
Without CI/CD: The Manual Process
It primarily involves the following steps:
- Development: Developers write code on their local machines.
- Integration: Periodically, developers merge their changes into a shared main branch. This could be done at the end of a sprint or after a feature is complete.
- Testing: Once code is integrated, it’s manually handed off to a Quality Assurance (QA) team. The QA team tests the code in a separate environment to ensure it works as expected.
- Deployment: Once the QA team signs off, the code is handed off to an operations team to deploy to a production environment.
Below were the problems faced without CI/CD
- Integration Hell: As developers work in isolation, integrating code becomes a painful process. Merging code from different teams can result in conflicts and bugs. Which result in delays in release cycles and increased debugging time.
- Lack of automation in testing: Manual testing is time-consuming and error-prone. QA teams might miss out on certain test cases. This can result in undetected bugs sneaking into production, affecting the user experience and trust.
- Inconsistent Environments: Development, testing, and production environments might not be consistent. A feature might work in development but break in production due to environmental differences. This can lead to unpredictable behavior in production and increased troubleshooting time.
- Manual Deployment Risks: Manual deployments are prone to human error. A missed step or incorrect configuration can cause outages. This can lead to downtime, a loss of user trust, and potential financial losses.
- Other issues can be slow release cycles, scalability issues, and a lack of transparency.
So let’s understand how Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment emerge as solutions.
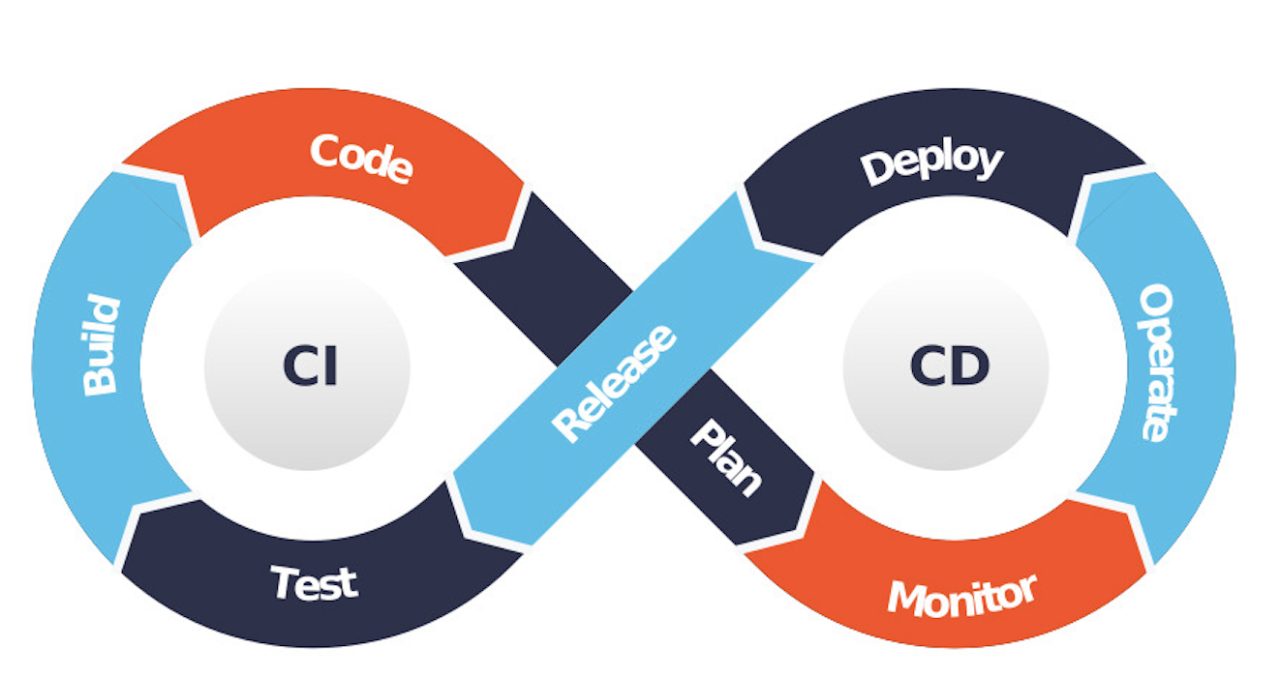
Continuous Integration (CI)
Continuous Integration is the practice of frequently integrating code changes into the main branch of a repository. Instead of waiting for days or weeks to merge feature branches into the main branch, CI promotes multiple integrations daily. Each integration is automatically verified by means of various levels of automated tests to detect errors as quickly as possible.
Benefits:
- Detects errors early, making them easier to fix.
- Encourages developers to share their code and integrate often.
- Reduces integration challenges because you’re integrating smaller changes.